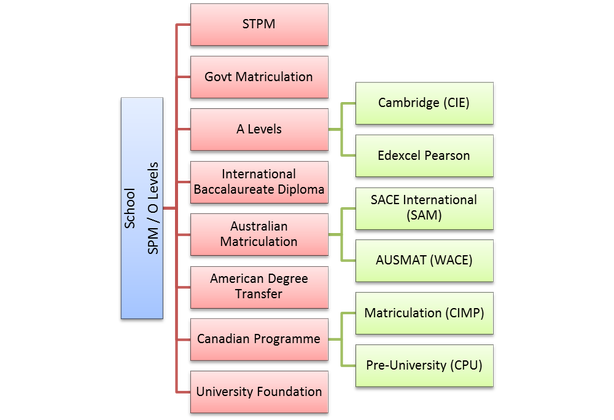
Pre-UniversityOnce you have completed secondary education and aspire for a university education, you are faced with many options, which we have called ‘Pre-university’ options. These are also sometimes known as Year 12, or bridging programmes or preparatory programmes. The diagram below captures most of the popular options available in Malaysia.
|
To find out more about each board and help you decide whether to do the CIE or Edexcel exam, see the links below. |
A Levels
In Malaysia, international schools offering the A Levels programme may offer students a choice of subjects and also a choice of exam boards: Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) and Pearson Edexcel. Both boards offer qualifications that are internationally recognised and accepted by colleges and universities around the world.
Exam boards are organisations that offer qualifications to students and it is their job to produce exam papers, mark your work and award your grade.
To find out more about each board and help you decide whether to do the CIE or Edexcel exam, see the links below.
Curriculum and recognition: The A levels is recognised worldwide and thousands of learners gain places at leading universities every year with the A level qualification. The syllabuses develop a deep understanding of subjects and independent thinking skills. Most students study three to four A level subjects, but institutions will provide guidance on this to help students get into the university and course of their choice.
Age and Duration: Although aimed at 16 – 19 year olds, they can be taken at any age, provided you have completed your GCSEs or SPM or equivalent. A Level programmes offered in Malaysia typically run between 15 to 24 months. They are made up of 2 parts: 1) AS (Advanced Subsidiary) and 2) A2.
Assessment: Assessments are exam-based. Previously, AS marks contributed towards the final A Level grades, but under the 2015 reforms, AS marks no longer have any impact on the final A-level grade. Instead, this final grade is decided by exams taken at the end of the A2 year. Nevertheless, the AS Level gives learners valuable feedback on their performance, identifying strengths and weaknesses before they complete the A2 stage.
Grading: Each subject that a learner takes receives a separate grade. Grades are benchmarked using internationally recognised grades, which have clear guidelines to explain the standards of achievement. The A Level is reported on a grade scale from A* (highest) to E (minimum required performance).
Exam boards are organisations that offer qualifications to students and it is their job to produce exam papers, mark your work and award your grade.
To find out more about each board and help you decide whether to do the CIE or Edexcel exam, see the links below.
- Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) - http://www.cie.org.uk/
- Pearson Edexcel - http://qualifications.pearson.com/en/home.html
Curriculum and recognition: The A levels is recognised worldwide and thousands of learners gain places at leading universities every year with the A level qualification. The syllabuses develop a deep understanding of subjects and independent thinking skills. Most students study three to four A level subjects, but institutions will provide guidance on this to help students get into the university and course of their choice.
Age and Duration: Although aimed at 16 – 19 year olds, they can be taken at any age, provided you have completed your GCSEs or SPM or equivalent. A Level programmes offered in Malaysia typically run between 15 to 24 months. They are made up of 2 parts: 1) AS (Advanced Subsidiary) and 2) A2.
Assessment: Assessments are exam-based. Previously, AS marks contributed towards the final A Level grades, but under the 2015 reforms, AS marks no longer have any impact on the final A-level grade. Instead, this final grade is decided by exams taken at the end of the A2 year. Nevertheless, the AS Level gives learners valuable feedback on their performance, identifying strengths and weaknesses before they complete the A2 stage.
Grading: Each subject that a learner takes receives a separate grade. Grades are benchmarked using internationally recognised grades, which have clear guidelines to explain the standards of achievement. The A Level is reported on a grade scale from A* (highest) to E (minimum required performance).
INTERNATIONAL BACCALAUREATE DIPLOMA PROGRAMME
Recognition: Although the International Baccalaureate (IB) is not as well-known as the A Levels, as of 22 May 2015, there were 2,795 schools offering the Diploma Programme (DP) in 143 different countries worldwide.
Age and Duration: The International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) is for students aged 16-19, and typically runs for 2 years.
Curriculum: The programme aims to develop students who have excellent breadth and depth of knowledge – students who flourish physically, intellectually, emotionally and ethically.
To encourage breadth and depth, IB DP offers subjects at the Standard Level (SL) so students are exposed to a range of disciplines and also subjects at the Higher Level (HL) so students can explore specific areas of personal interest in greater depth. SL courses are recommended to have at least 150 hours of instructional time, and HL courses are recommended to have at least 240 instructional hours. It must be noted that the assessment criteria are equally demanding for both levels, and SL exams are marked and standardized with the same rigour as all IB coursework.
The curriculum is made up of the DP core and six subject groups.
The DP core is made up of the three required components and aims to broaden students’ educational experience and challenge them to apply their knowledge and skills. The three core elements are:
The six subject groups are listed below with an example of the different courses within each subject group:
Assessment: IB DP uses both external (exams) and internal assessment (teacher assessment of fieldwork, laboratory work, artistic performances, etc. ). In addition, the DP core can collectively contribute up to 3 additional points towards the overall Diploma score.
Student results are determined by performance against set standards, not by each student's position in the overall rank order. In the DP, students receive grades ranging from 7 to 1, with 7 being highest. Students receive a grade for each DP course attempted. A student’s final Diploma result score is made up of the combined scores for each subject. The diploma is awarded to students who gain at least 24 points, subject to certain minimum levels of performance including successful completion of the three essential elements of the DP core.
Age and Duration: The International Baccalaureate® (IB) Diploma Programme (DP) is for students aged 16-19, and typically runs for 2 years.
Curriculum: The programme aims to develop students who have excellent breadth and depth of knowledge – students who flourish physically, intellectually, emotionally and ethically.
To encourage breadth and depth, IB DP offers subjects at the Standard Level (SL) so students are exposed to a range of disciplines and also subjects at the Higher Level (HL) so students can explore specific areas of personal interest in greater depth. SL courses are recommended to have at least 150 hours of instructional time, and HL courses are recommended to have at least 240 instructional hours. It must be noted that the assessment criteria are equally demanding for both levels, and SL exams are marked and standardized with the same rigour as all IB coursework.
The curriculum is made up of the DP core and six subject groups.
The DP core is made up of the three required components and aims to broaden students’ educational experience and challenge them to apply their knowledge and skills. The three core elements are:
- Theory of knowledge, in which students reflect on the nature of knowledge and on how we know what we claim to know.
- The extended essay, which is an independent, self-directed piece of research, finishing with a 4,000-word paper.
- Creativity, activity, service, in which students complete a project related to those three concepts.
The six subject groups are listed below with an example of the different courses within each subject group:
- Studies in language and literature (e.g. English)
- Language acquisition (e.g. French)
- Individuals and societies (e.g. History)
- Sciences (e.g. Chemistry)
- Mathematics (e.g. Mathematics)
- The arts (e.g. Music)
Assessment: IB DP uses both external (exams) and internal assessment (teacher assessment of fieldwork, laboratory work, artistic performances, etc. ). In addition, the DP core can collectively contribute up to 3 additional points towards the overall Diploma score.
Student results are determined by performance against set standards, not by each student's position in the overall rank order. In the DP, students receive grades ranging from 7 to 1, with 7 being highest. Students receive a grade for each DP course attempted. A student’s final Diploma result score is made up of the combined scores for each subject. The diploma is awarded to students who gain at least 24 points, subject to certain minimum levels of performance including successful completion of the three essential elements of the DP core.
WESTERN AUSTRALIAN MATRICULATION (AUSMAT OR WACE)
Recognition: The WACE or Western Australia Certificate of Education is commonly known as AUSMAT in Malaysia and as the name suggests, is offered by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority (SCSA) of Western Australia. It is a world recognised pre-university program that provides a seamless transition into universities across Australia and around the world, including Ivy League universities in the United States of America and the United Kingdom.
AUSMAT opens pathways to a wide range of career opportunities. The one-year AUSMAT program is the same as the Year 12 program offered in Western Australia. Successful students receive the Western Australian Certificate of Education (WACE), issued by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority (the Authority), on behalf of the Western Australian Government.
Age and Duration: Aimed at students aged 16-19, AUSMAT is delivered in 10 – 18 months in Malaysia, depending on when you embark on the programme.
Curriculum: The AUSMAT program is dynamic, relevant, balanced and academically challenging. AUSMAT prepares students for a variety of career paths, including medicine, dentistry, finance, business, information technology, science, law, engineering and the arts. Students develop communication skills, self-discipline, and respect for themselves, their peers and the world. As well as a well-rounded curriculum, students develop skills in teamwork, self-expression and personal development.
Students are usually required to select five AUSMAT courses with at least one from List A which comprises courses in the field of Arts, Languages and Social Sciences (like Business Management, ESL, Economics etc.) and one from List B which are courses in the area of Mathematics, Science and Technology (e.g. Mathematics, Psychology Accounting and Finance etc.) . Students must also complete two units of an English course and obtain at least one C grade in English.
Assessment: Assessment comprises 50% school assessments and 50% external examinations. In school assessments, lecturers develop tasks that meet the requirements of the course syllabus. Tasks may include assignments, laboratory work, quizzes, tests and projects. There is, in addition, an external examination for each course. Examinations are conducted every November. Independent markers mark the examination papers. They are the same markers who assess the exam papers of Western Australian students.
Grading: For students seeking university entrance, an Australian Tertiary Admission Rank (ATAR) is calculated using the best four course results. The ATAR score reports your rank position relative to all other students. (For e.g., an ATAR score of 90.0 means that you performed better than 90% of your peers). The ATAR is used by university admission centres around the world to process applications for admission to most undergraduate courses.
AUSMAT opens pathways to a wide range of career opportunities. The one-year AUSMAT program is the same as the Year 12 program offered in Western Australia. Successful students receive the Western Australian Certificate of Education (WACE), issued by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority (the Authority), on behalf of the Western Australian Government.
Age and Duration: Aimed at students aged 16-19, AUSMAT is delivered in 10 – 18 months in Malaysia, depending on when you embark on the programme.
Curriculum: The AUSMAT program is dynamic, relevant, balanced and academically challenging. AUSMAT prepares students for a variety of career paths, including medicine, dentistry, finance, business, information technology, science, law, engineering and the arts. Students develop communication skills, self-discipline, and respect for themselves, their peers and the world. As well as a well-rounded curriculum, students develop skills in teamwork, self-expression and personal development.
Students are usually required to select five AUSMAT courses with at least one from List A which comprises courses in the field of Arts, Languages and Social Sciences (like Business Management, ESL, Economics etc.) and one from List B which are courses in the area of Mathematics, Science and Technology (e.g. Mathematics, Psychology Accounting and Finance etc.) . Students must also complete two units of an English course and obtain at least one C grade in English.
Assessment: Assessment comprises 50% school assessments and 50% external examinations. In school assessments, lecturers develop tasks that meet the requirements of the course syllabus. Tasks may include assignments, laboratory work, quizzes, tests and projects. There is, in addition, an external examination for each course. Examinations are conducted every November. Independent markers mark the examination papers. They are the same markers who assess the exam papers of Western Australian students.
Grading: For students seeking university entrance, an Australian Tertiary Admission Rank (ATAR) is calculated using the best four course results. The ATAR score reports your rank position relative to all other students. (For e.g., an ATAR score of 90.0 means that you performed better than 90% of your peers). The ATAR is used by university admission centres around the world to process applications for admission to most undergraduate courses.
WESTERN AUSTRALIAN MATRICULATION (AUSMAT OR WACE)
Recognition: The WACE or Western Australia Certificate of Education is commonly known as AUSMAT in Malaysia and as the name suggests, is offered by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority (SCSA) of Western Australia. It is a world recognised pre-university program that provides a seamless transition into universities across Australia and around the world, including Ivy League universities in the United States of America and the United Kingdom.
AUSMAT opens pathways to a wide range of career opportunities. The one-year AUSMAT program is the same as the Year 12 program offered in Western Australia. Successful students receive the Western Australian Certificate of Education (WACE), issued by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority (the Authority), on behalf of the Western Australian Government.
Age and Duration: Aimed at students aged 16-19, AUSMAT is delivered in 10 – 18 months in Malaysia, depending on when you embark on the programme.
Curriculum: The AUSMAT program is dynamic, relevant, balanced and academically challenging. AUSMAT prepares students for a variety of career paths, including medicine, dentistry, finance, business, information technology, science, law, engineering and the arts. Students develop communication skills, self-discipline, and respect for themselves, their peers and the world. As well as a well-rounded curriculum, students develop skills in teamwork, self-expression and personal development.
Students are usually required to select five AUSMAT courses with at least one from List A which comprises courses in the field of Arts, Languages and Social Sciences (like Business Management, ESL, Economics etc.) and one from List B which are courses in the area of Mathematics, Science and Technology (e.g. Mathematics, Psychology Accounting and Finance etc.) . Students must also complete two units of an English course and obtain at least one C grade in English.
Assessment: Assessment comprises 50% school assessments and 50% external examinations. In school assessments, lecturers develop tasks that meet the requirements of the course syllabus. Tasks may include assignments, laboratory work, quizzes, tests and projects. There is, in addition, an external examination for each course. Examinations are conducted every November. Independent markers mark the examination papers. They are the same markers who assess the exam papers of Western Australian students.
Grading: For students seeking university entrance, an Australian Tertiary Admission Rank (ATAR) is calculated using the best four course results. The ATAR score reports your rank position relative to all other students. (For e.g., an ATAR score of 90.0 means that you performed better than 90% of your peers). The ATAR is used by university admission centres around the world to process applications for admission to most undergraduate courses.
AUSMAT opens pathways to a wide range of career opportunities. The one-year AUSMAT program is the same as the Year 12 program offered in Western Australia. Successful students receive the Western Australian Certificate of Education (WACE), issued by the School Curriculum and Standards Authority (the Authority), on behalf of the Western Australian Government.
Age and Duration: Aimed at students aged 16-19, AUSMAT is delivered in 10 – 18 months in Malaysia, depending on when you embark on the programme.
Curriculum: The AUSMAT program is dynamic, relevant, balanced and academically challenging. AUSMAT prepares students for a variety of career paths, including medicine, dentistry, finance, business, information technology, science, law, engineering and the arts. Students develop communication skills, self-discipline, and respect for themselves, their peers and the world. As well as a well-rounded curriculum, students develop skills in teamwork, self-expression and personal development.
Students are usually required to select five AUSMAT courses with at least one from List A which comprises courses in the field of Arts, Languages and Social Sciences (like Business Management, ESL, Economics etc.) and one from List B which are courses in the area of Mathematics, Science and Technology (e.g. Mathematics, Psychology Accounting and Finance etc.) . Students must also complete two units of an English course and obtain at least one C grade in English.
Assessment: Assessment comprises 50% school assessments and 50% external examinations. In school assessments, lecturers develop tasks that meet the requirements of the course syllabus. Tasks may include assignments, laboratory work, quizzes, tests and projects. There is, in addition, an external examination for each course. Examinations are conducted every November. Independent markers mark the examination papers. They are the same markers who assess the exam papers of Western Australian students.
Grading: For students seeking university entrance, an Australian Tertiary Admission Rank (ATAR) is calculated using the best four course results. The ATAR score reports your rank position relative to all other students. (For e.g., an ATAR score of 90.0 means that you performed better than 90% of your peers). The ATAR is used by university admission centres around the world to process applications for admission to most undergraduate courses.
A Levels
testing
want to check if I can put a coloured box here and another accordion here
want to check if I can put a coloured box here and another accordion here
View more institutions
Taylors
Segi etc.
Segi etc.
|
Text in a coloured box
plus image in a coloured box |